How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a question many aspiring pilots ask. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from pre-flight checks and safety protocols to mastering flight controls and capturing stunning aerial footage. We’ll explore various flight modes, essential maintenance procedures, and the crucial legal and ethical considerations that ensure responsible drone use.
Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your skills, this comprehensive resource will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly.
Understanding drone operation involves more than just familiarizing yourself with the controls; it requires a deep understanding of safety regulations, flight mechanics, and post-processing techniques. This guide aims to provide a structured approach to learning, covering each aspect systematically to build a strong foundation in safe and responsible drone piloting.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before embarking on any drone flight, a thorough pre-flight checklist and adherence to safety procedures are paramount. This ensures both the safe operation of the drone and the safety of those around you. Neglecting this crucial step can lead to accidents and potential legal repercussions.
Drone Pre-Flight Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection involves a systematic check of all drone components. This helps identify potential issues before they become problems during flight.
| Item | Check | Status (Pass/Fail) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Inspect for cracks, damage, or imbalance. | Pass/Fail | Replace damaged propellers immediately. |
| Battery | Check battery level and ensure proper connection. | Pass/Fail | Use only manufacturer-approved batteries. |
| Gimbal (if applicable) | Verify gimbal movement and functionality. | Pass/Fail | Ensure gimbal is securely mounted. |
| Camera | Check camera lens for cleanliness and functionality. | Pass/Fail | Clean the lens with a microfiber cloth. |
| Sensors | Ensure all sensors (GPS, IMU, etc.) are functioning correctly. | Pass/Fail | Run a sensor calibration if necessary. |
| Airframe | Inspect the drone body for any damage or loose parts. | Pass/Fail | Tighten any loose screws or bolts. |
| Radio Control | Test the remote controller and ensure proper connection with the drone. | Pass/Fail | Check battery level of the remote controller. |
Understanding and Adhering to Local Drone Regulations
Operating a drone requires understanding and adhering to local laws and regulations. These regulations vary by location and are designed to ensure public safety and prevent airspace conflicts. Ignorance of these rules can result in hefty fines or legal action.
- Registration: Many countries require drone registration with the relevant aviation authority.
- Airspace Restrictions: Flying near airports, military bases, or other restricted airspace is generally prohibited. Check the airspace map before flying.
- Altitude Limits: Most jurisdictions impose limits on how high a drone can fly.
- Privacy Concerns: Operating a drone near private property without permission is often a violation of privacy laws.
- Visual Line of Sight (VLOS): In many places, drones must be kept within the operator’s visual line of sight at all times.
Safety Briefing for First-Time Drone Operators
A comprehensive safety briefing is essential for first-time drone operators. This briefing should cover potential hazards and emergency procedures.
- Emergency Procedures: Explain how to handle unexpected situations such as loss of control, low battery, or malfunctioning components. The return-to-home function should be emphasized.
- Potential Hazards: Discuss potential hazards like collisions with objects, people, or animals, and the risks associated with flying in adverse weather conditions.
- Safe Flight Practices: Emphasize maintaining a safe distance from people and property, avoiding congested areas, and always flying responsibly.
Battery Safety and Charging Procedures
Drone batteries are powerful and require careful handling and charging. Improper handling can lead to fire or explosion.
- Only use manufacturer-approved chargers and batteries.
- Never leave batteries charging unattended.
- Charge batteries in a well-ventilated area.
- Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from flammable materials.
- Dispose of batteries properly according to local regulations.
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding drone controls and navigation is fundamental to safe and efficient operation. This section details the basic controls and provides guidance on various navigation techniques.
Basic Drone Controls
Most drones use a similar set of controls. Understanding these is crucial for safe operation.
- Throttle: Controls the altitude of the drone. Pushing the stick up increases altitude, pushing it down decreases altitude.
- Yaw: Controls the drone’s rotation around its vertical axis (turning left or right).
- Pitch: Controls the drone’s movement forward and backward.
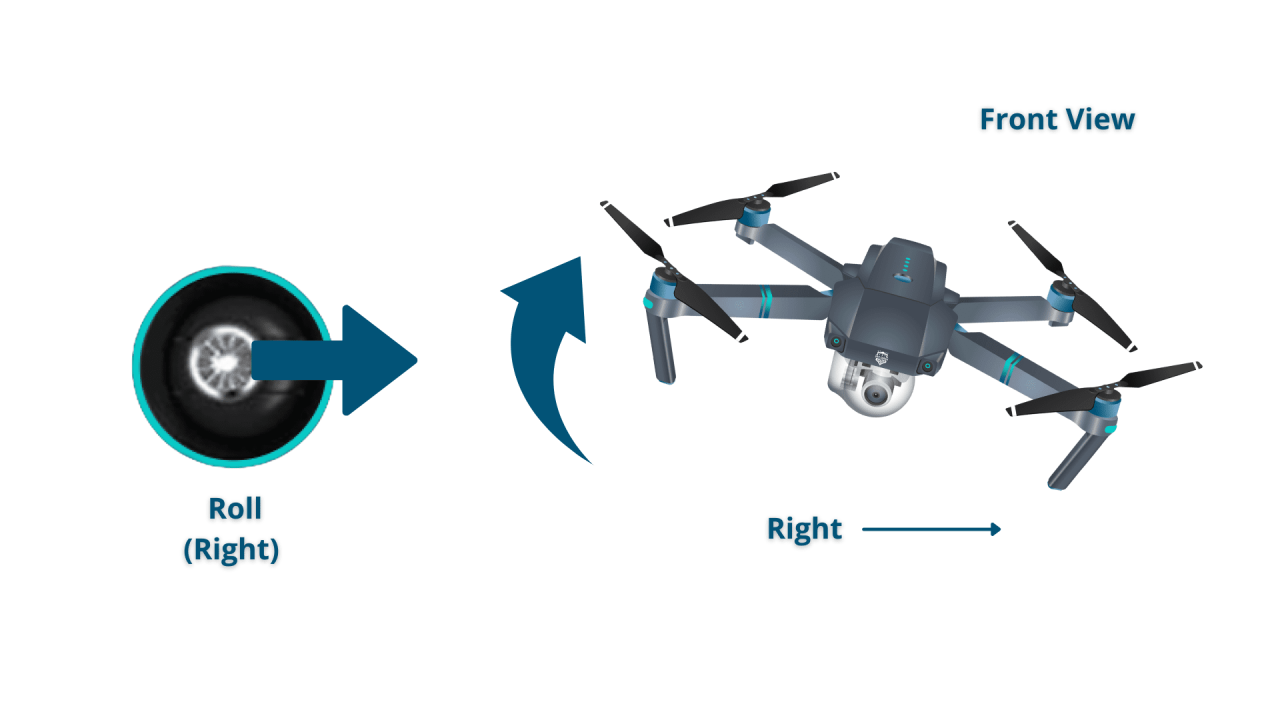
- Roll: Controls the drone’s movement left and right.
Drone Control Methods, How to operate a drone
Drones can be controlled through various methods, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
- Joystick-Based Control: Offers precise control and is often preferred by experienced pilots. It provides a more tactile and intuitive feel.
- App-Based Control: Offers a user-friendly interface, often with features like automated flight modes and simplified controls. It may be less precise than joystick control for complex maneuvers.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Procedures

Safe takeoff and landing procedures are critical for preventing accidents. Follow these steps for a smooth and controlled flight.
- Ensure the drone is fully charged and calibrated.
- Select an open, level area away from obstacles.
- Slowly increase throttle to lift off vertically.
- Maintain a stable hover before moving the drone.
- For landing, slowly decrease throttle until the drone gently touches down.
Drone Navigation in Different Environments
Navigating a drone in various environments requires different techniques and considerations.
- Open Fields: Easier navigation due to fewer obstacles. Focus on maintaining altitude and direction.
- Urban Areas: Requires careful planning and awareness of obstacles like buildings, trees, and power lines. Use lower altitudes and slower speeds.
- Windy Conditions: Adjust flight settings to compensate for wind. Maintain a stable altitude and be prepared for unexpected gusts.
Flight Modes and Features
Modern drones offer various flight modes and features that enhance control and capabilities. Understanding these modes and features is crucial for optimizing flight performance and safety.
Drone Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and automation.
| Flight Mode | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPS Mode | Relies on GPS signals for positioning and stability. | Stable flight, even in windy conditions. | Requires a strong GPS signal. |
| Attitude Mode | Maintains the drone’s attitude (orientation) relative to its starting position. | More responsive control. | Can drift over time without GPS assistance. |
| Sport Mode (if applicable) | Offers increased responsiveness and speed. | Faster maneuvers. | Requires more skill and precision. |
Autonomous Flight Features
Autonomous flight features enhance drone capabilities, but also come with limitations.
- Waypoint Navigation: Allows the drone to follow a pre-programmed path. Useful for creating cinematic shots or surveying large areas.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): Automatically returns the drone to its home point in case of signal loss or low battery. A critical safety feature.
Optimizing Flight Performance
Adjusting drone settings optimizes performance in different conditions.
- Windy Conditions: Reduce speed and increase sensitivity settings.
- Low Light Conditions: Reduce flight speed and ensure sufficient battery life.
Photography and Videography with Drones
Drones offer unique perspectives for capturing stunning aerial photos and videos. Mastering camera settings and composition techniques is key to achieving high-quality results.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Media
Achieving high-quality aerial photography and videography involves careful consideration of various factors.
- Lighting: The “golden hour” (sunrise and sunset) offers soft, warm lighting ideal for photography and videography.
- Composition: Utilize the rule of thirds, leading lines, and other compositional techniques to create visually appealing shots.
- Camera Settings: Adjust ISO, shutter speed, and aperture to optimize image quality in various lighting conditions.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Understanding camera settings allows for greater control over image quality.
- ISO: Controls the sensitivity of the camera sensor to light. Lower ISO values produce less noise but require more light.
- Shutter Speed: Controls the duration the camera’s sensor is exposed to light. Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower shutter speeds can create motion blur.
- Aperture: Controls the amount of light entering the camera lens. A wider aperture (lower f-stop number) allows more light in, resulting in a shallower depth of field.
Composing Compelling Aerial Shots

Creative composition enhances the visual appeal of aerial media.
- Rule of Thirds: Place key elements along imaginary lines that divide the frame into thirds.
- Leading Lines: Use natural lines (roads, rivers) to guide the viewer’s eye through the image.
- Symmetry and Patterns: Capture symmetrical scenes or repeating patterns for visually striking results.
Post-Processing Drone Footage
Post-processing enhances the quality and visual appeal of drone footage.
- Editing: Trim unwanted footage, add transitions, and adjust pacing.
- Color Grading: Adjust colors and contrast to enhance mood and atmosphere.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are essential for keeping your drone in optimal condition and extending its lifespan. This section Artikels key maintenance procedures and common troubleshooting steps.
Regular Drone Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule helps prevent malfunctions and extends the drone’s lifespan.
- Cleaning: Clean the drone body, propellers, and camera lens after each flight to remove dirt and debris.
- Component Checks: Regularly inspect all components for wear and tear, paying particular attention to propellers, motors, and the gimbal (if applicable).
- Firmware Updates: Keep the drone’s firmware updated to benefit from bug fixes and new features.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Troubleshooting
Understanding common malfunctions and troubleshooting steps minimizes downtime.
- Low Battery: Charge the battery fully.
- GPS Signal Loss: Relocate to an area with a stronger GPS signal.
- Motor Malfunction: Inspect motors for damage and replace if necessary.
- Propeller Damage: Replace damaged propellers.
Replacing Common Drone Parts
Replacing common parts requires careful attention to detail.
- Propellers: Ensure proper alignment and secure fastening.
- Batteries: Use only manufacturer-approved batteries.
Troubleshooting Flowchart
A flowchart provides a structured approach to troubleshooting drone malfunctions.
(Note: A visual flowchart would be included here, detailing steps like checking battery, signal strength, propellers, etc., ultimately leading to solutions or the need for professional repair.)
Legal and Ethical Considerations: How To Operate A Drone
Operating a drone responsibly involves understanding and adhering to both legal and ethical guidelines. This section highlights key legal requirements and ethical considerations to ensure safe and responsible drone operation.
Legal Requirements for Drone Operation
Legal requirements for drone operation vary significantly across jurisdictions. Failure to comply can lead to substantial fines and legal penalties.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning the basics is crucial for safe and effective operation, and a great resource to begin your journey is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. Once you’ve grasped the fundamentals, you can explore more advanced techniques and features, ultimately enhancing your drone piloting skills.
- Registration: Many countries mandate drone registration with the relevant aviation authority.
- Licensing: Some jurisdictions require operators to obtain a license or permit before operating a drone.
- Airspace Restrictions: Flying near airports, military bases, or other restricted airspace is strictly prohibited.
- Privacy Laws: Operating a drone near private property without permission can be a violation of privacy laws.
Ethical Considerations in Drone Operation
Ethical considerations play a crucial role in responsible drone operation.
- Privacy: Respect the privacy of individuals and avoid filming without their consent.
- Safety: Prioritize the safety of yourself and others. Avoid flying near people or objects.
- Environmental Impact: Be mindful of the environment and avoid disturbing wildlife or natural habitats.
Best Practices for Responsible Drone Operation
Responsible drone operation involves a commitment to safety, privacy, and ethical conduct.
- Always maintain visual line of sight.
- Avoid flying in adverse weather conditions.
- Respect private property and airspace restrictions.
- Obtain necessary permissions before flying in restricted areas.
Resources for Drone Regulations and Ethical Guidelines
Numerous resources provide information on drone regulations and ethical guidelines.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating this process requires learning about safety protocols and airspace regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone and become a confident pilot. Remember, responsible drone operation is crucial for safe and enjoyable flights.
- Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) website (for US operators): Provides information on drone regulations and registration.
- European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) website (for EU operators): Offers guidance on drone regulations and safety.
- Local aviation authorities: Check with your local aviation authority for specific regulations in your area.
Mastering the art of drone operation is a journey of continuous learning and responsible practice. From understanding the fundamentals of pre-flight checks and navigating diverse flight modes to capturing breathtaking aerial visuals and adhering to legal and ethical guidelines, this guide has provided a comprehensive framework for safe and effective drone piloting. Remember, responsible drone operation is not just about technical proficiency; it’s about respecting airspace regulations, prioritizing safety, and appreciating the ethical implications of this powerful technology.
By integrating these principles into your flying practices, you can contribute to the responsible growth and advancement of the drone community.
Common Queries
What type of drone is best for beginners?
User-friendly drones with GPS, return-to-home features, and intuitive controls are ideal for beginners. Many reputable brands offer models specifically designed for ease of use.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Compass calibration should be performed before each flight, especially if you’ve flown near sources of magnetic interference.
What is the best way to store drone batteries?
Store drone batteries in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and heat sources, at approximately 50% charge when not in use for extended periods.
What should I do if my drone loses signal?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. If signal is lost, the drone will attempt to return to its takeoff point. If RTH fails, try to visually locate the drone and retrieve it.
